Mitsubishi L200 Workshop Manuals and Repair Manuals
Every Manual available online - found by our community and shared for FREE. Enjoy!
Mitsubishi L200
The L200 is a compact-sized pickup truck built and sold by Mitsubishi Motors. Although in most markets it’s known as the L200, it’s a truck with many different names. In its homeland of Japan, you can find it under the Mitsubishi Triton or the Mitsubishi Forte monikers. From 1991, Mitsubishi changed the L200’s name for the domestic market from Forte to the Strada. Because of Mitsubishi’s partnership with Chrysler, you can also find the L200 in the United States under the Dodge Ram 50 and the Plymouth Arrow nameplates. Mitsubishi’s name for the L200 in the US up until 1996 was the Mighty Max.
Other common names the L200 goes by include but are not limited to Rodeo, Storm, Magnum, Colt, and the L200 Strakar. Although the naming strategy is confusing and somewhat overwhelming, all these different model names essentially represent the same vehicle: a rebadged Mitsubishi L200 destined for various markets. Given how popular and successful the L200’s become over the years, we thought we’d look at its history, the different generations, as well as what made each one of them so special.
First Generation – 1978 to 1986

The first generation L200, also known as the Forte (L020), made its debut in Japan, in 1978. It was initially offered with a 1.6-liter four-cylinder engine making 92 horsepower, but Mitsubishi later introduced a more powerful 2.0-liter engine and a modern four-wheel-drive system. In 1986, Mitsubishi canceled the Forte in its domestic market, a decision that would last for the subsequent five years before they re-introduced it again in 1991.
Export variants of the L200 came with either a 93 horsepower 2.0-liter engine or a larger 2.6-liter four-cylinder making 105 horsepower. Some markets also got the 2.3-liter 4D55 diesel engine developing 67 horsepower, as well as the 1.6-liter Saturn unit. Target markets received a naked cab and chassis version in addition to the different powerplant units.
The first L200 was extremely sophisticated for its time, especially for a pickup truck. It had front disc brakes, recirculating ball steering, and coil spring front suspension. The 4WD system which was introduced in 1981 featured a torsion-bar setup in the front. The 4WD system consisted of three different positions: high-range 2WD, high-range 4WD, and low-range 4WD for off-roading or towing heavy trailers over rough terrain.
The first L200 sold on North American soil wasn’t even sold under the Mitsubishi nameplate. Dodge introduced the Ram D-50 in 1979, a pickup that was essentially a rebadged Mitsubishi L200 underneath. Plymouth did a similar thing with the Plymouth Arrow truck. Later on, Mitsubishi debuted the Mighty Max in the US in 1982, effectively axing Plymouth’s Arrow. When 4WD was introduced, Dodge decided to rename their truck to the Ram 50 instead of the D-50 to mark this significant milestone. Some US models also came with a diesel engine, producing 80 horsepower and 125 lb-ft of torque thanks to the TC05 non-wastegated turbo. In 1984 Mitsubishi substituted the TC05 for a TD04, a wastegated turbo, raising the total power output to 86 horsepower and 134 lb-ft of torque.
Second Generation – 1986 to 1996
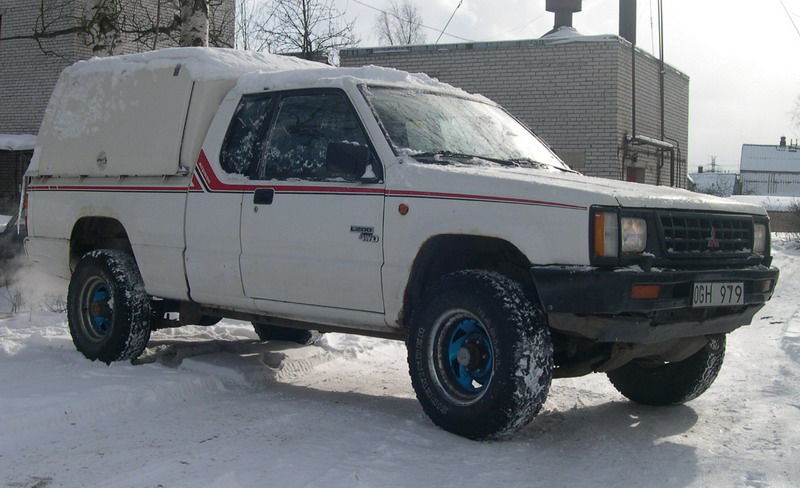

Although Japanese manufacturers like to introduce new generations in their domestic market first, because the L200 ceased production in Japan for five whole years, most export markets saw the brand-new, second-gen L200 at around the same time. Despite the fact that there were 4 different gasoline and 3 different diesel engines on offer depending on the market, US-bound L200 variants were only offered with a 92 horsepower 2.0-liter four-cylinder or the venerable 2.6-liter 4G54 making 109 horsepower. Mitsubishi’s 4WD was an optional extra, and customers had a choice between several different bed lengths as well as an extended or a double cab.
Not only was the second generation L200 a lot bigger than the first, but it was also more refined. Mitsubishi may have debuted a fairly crude and utilitarian truck in 1986, but over time they introduced several different versions for people who wanted slightly more comfort and luxury. In Australia, they even introduced a V6 engine with 122 horsepower, but it wasn’t received particularly well by the general public, mostly because it couldn’t tow as much as the diesels, but also because it was a ticking time-bomb thanks to an engine design flaw.
In 1987 Dodge introduced the brand-new Dakota, the Ram 50’s official successor. Because the Ram 50 received a major facelift that same year, and probably because it was slightly smaller than the Dodge Dakota, Chrysler decided to continue selling both models side by side for another 7 years. In 1994, the Ram 50 ceased to exist. With the brand-new generation just around the corner, 1996 also marked the death of the Mitsubishi Mighty Max, the original L200. Poor sales killed it off, and it never received a successor for the North American market.
Third Generation – 1996 to 2006
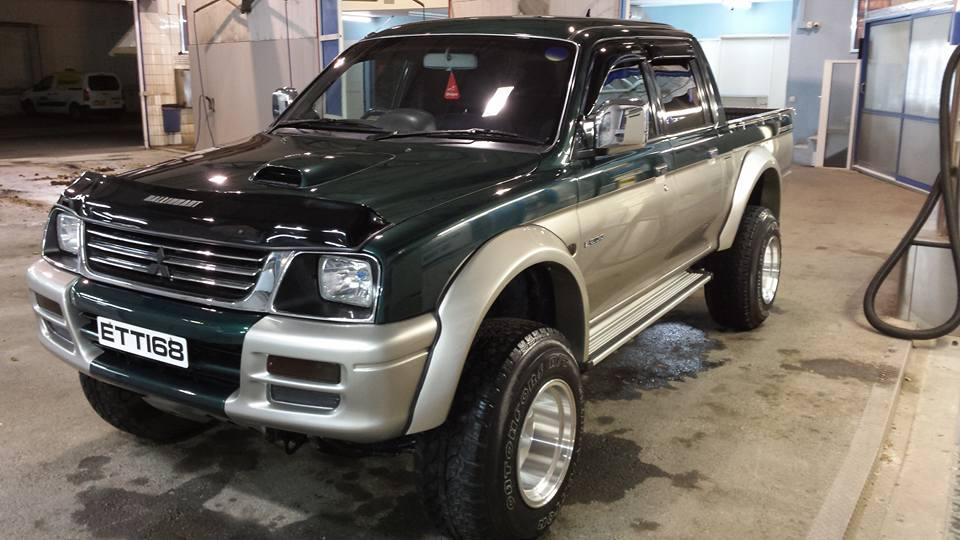

The third-gen L200, now known as the K50/K60/K70, hit the market in 1996. The old 2.6-liter diesel was replaced with a new, slightly smaller 2.4-liter turbodiesel, but despite the downsizing, it had a much healthier output of 145 horsepower. Other engine choices ranged from 2.0-liter to 3.0-liter for the gasoline units, and from 2.5-liter to 2.8-liter for the diesels. In 2001 the L200 received a fairly significant upgrade. It got redesigned headlights, different bumpers, and other aesthetic updates.
The Mitsubishi Triton (L200) also spawned the Mitsubishi Challenger in 1996. Essentially a modified variant of the L200 built as a passenger pickup truck, the Challenger was only offered in Japan. Realizing what a potential sales hit it might be, Mitsubishi started exporting it later on and marketed it as the Montero Sport, the Pajero Sport, the Shogun Sport, and the Nativa, depending on the market. The Challenger used a lot of the same body panels as the ones found on the Strada pickup truck, and it had the same wheelbase as the second-gen Pajero. In Thailand, it was known as the Mitsubishi Strada G-Wagon.
Fourth Generation – 2005 to 2014
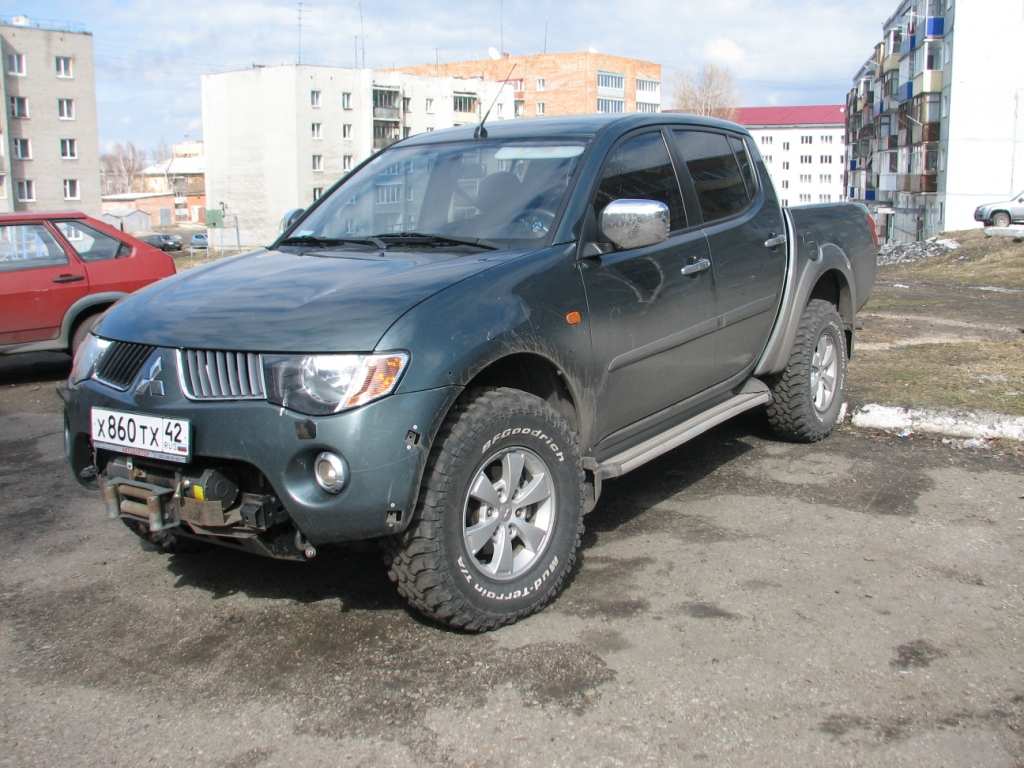

The fourth-gen L200 made its official debut in 2005. Although assembly takes place in Brazil, Thailand, and South Africa, the pickup is built exclusively in Thailand. From there, it gets exported to around 140 different global markets. Most L200 pickups of this generation carry a 2.5-liter turbodiesel engine under the hood, but a decent chunk of them can also be found with Mitsubishi’s 2.4-liter four-cylinder gasoline engine. In Japan, the only engine available in the Triton was a 3.5-liter V6 with 186 horsepower. The V6 is a rare sight in markets outside of Japan.
All V6 engines come mated to a 4-speed automatic transmission, but there were 5-speed auto and 5-speed manual transmissions on offer too (mostly found on the diesels). Despite its significant success overseas, the Triton never caught on in Japan as most workmen preferred small vans and even station wagons to a large pickup.
Fifth Generation – 2015 to present
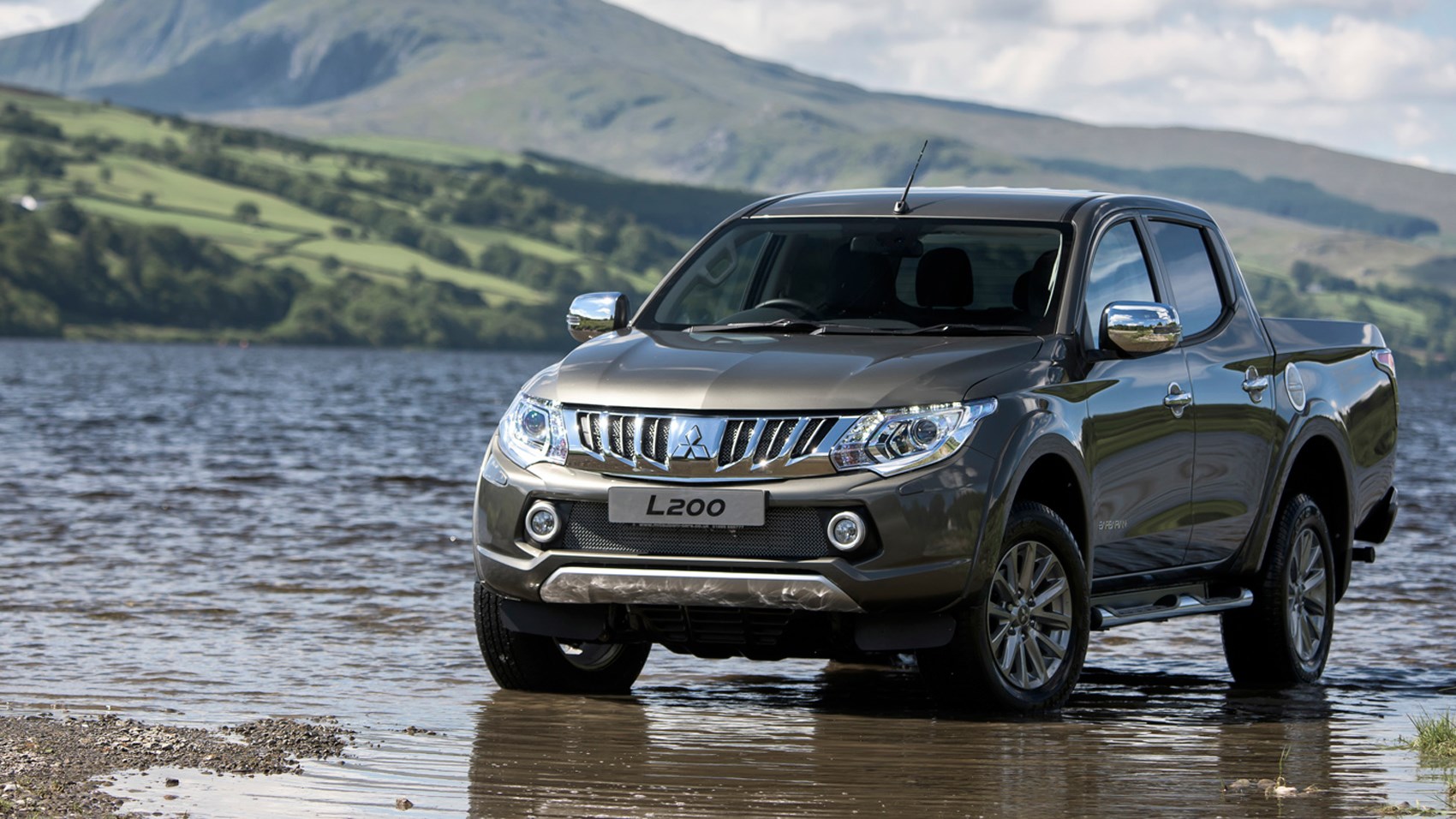

In 2015, ten years after the fourth-gen L200 made its debut, Mitsubishi unveiled its completely redesigned pickup truck. The new model shares most of its components with the Fiat Fullback, a rebadged L200 intended for European and Middle Eastern markets. Although Fiat has no plans of introducing the Fullback to the US due to the chicken tax, Ram rebadged the Triton as the Ram 1200 and is currently marketing it in the Middle East. Mitsubishi have no plans of re-introducing the truck to their domestic market due to abysmal sale figures of previous generations and a lack of need for pickups in Japan.
The fifth-gen L200 comes with a single gasoline engine and three different diesel units: a 2.2-liter, a 2.4-liter MIVEC, and a revised 2.5-liter ‘4D56’ four-cylinder. There are two manuals, a five and a six-speed, and two different automatics, also a 5 and a 6-speed. The former is a normal auto, but the latter is a robust AISIN box with more towing capabilities and better off-road performance.
At last year’s Thailand International Motor Expo, Mitsubishi updated the L200 for the 2019 model year, giving it a new front fascia, a new taillight design, and minor interior updates. The facelifted fifth-gen L200 is easily the most refined and easy-to-live-with L200 to date, taking most styling cues from its bigger passenger cousin, the Pajero/Montero Sport. It has the same wheelbase as its predecessor, the KA/KB L200, but it’s 7 inches (17cm) longer and 3 inches (7cm) wider.
Mitsubishi L200 FAQ's
How do I adjust the headlights on my Mitsubishi L200?
How do I change the cabin air filter in my Mitsubishi L200?
How do I change the oil in my Mitsubishi L200?
How do I check and top up the brake fluid in my Mitsubishi L200?
How do I check the transmission fluid level in my Mitsubishi L200?
How do I jump-start my Mitsubishi L200?
How do I replace a blown fuse in my Mitsubishi L200?
How do I replace a broken headlight bulb in my Mitsubishi L200?
How do I replace the serpentine belt in my Mitsubishi L200?
How do I replace the windshield wipers on my Mitsubishi L200?
How do I reset the maintenance reminder light in my Mitsubishi L200?
How do I troubleshoot a faulty power window in my Mitsubishi L200?
How often should I replace the air filter in my Mitsubishi L200?
What is the recommended tire pressure for a Mitsubishi L200?
What type of coolant should I use in my Mitsubishi L200?
Get notified for new manuals?
We'll send you a quick email when a new Mitsubishi L200 manual is added.
Mitsubishi L200 Manuals Index
Mitsubishi L200 Workshop Manual
-

- Mitsubishi L200 1997 Workshop Manual BRM
- (146 Pages)
- (Free)
-

- Mitsubishi L200 2012 Workshop Manual
- (3,818 Pages)
- (Free)
-

- Mitsubishi L200 Workshop Manual
- (558 Pages)
- (Free)
Mitsubishi L200 Owners Manual
-

- Mitsubishi L200 Owners Manual
- (369 Pages)
- (Free)
Mitsubishi L200 Misc Document
-

- Mitsubishi L200 1996 Repair Manual
- (1,723 Pages)
- (Free)
Related Models